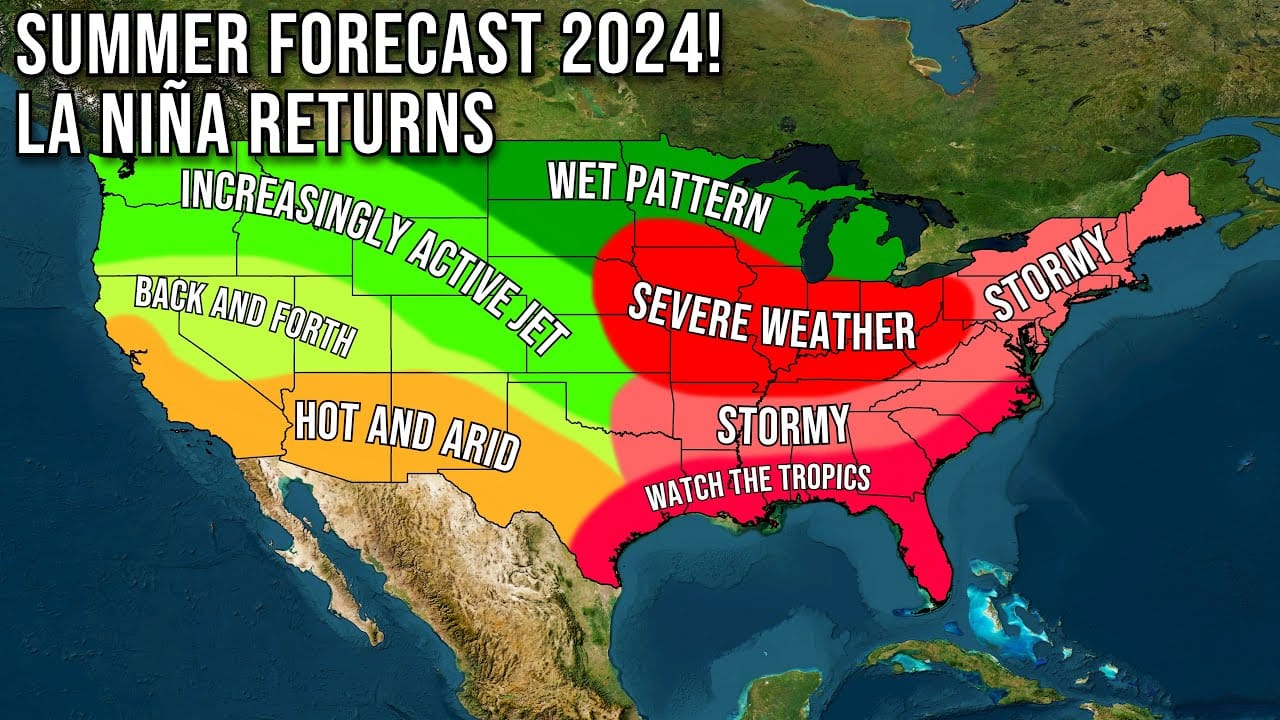
La Niña Returns: The Impact of the 2024 Rainy Season on Agriculture and Infrastructure
As we move into the final months of 2024, weather experts are keeping a close watch on the upcoming rainy season. The forecast calls for notable shifts in precipitation patterns, with some regions bracing for heavy rains while others prepare for the lingering effects of previous climate events. Understanding the global implications of these weather patterns, including the influence of La Niña and El Niño, is crucial for sectors such as agriculture, infrastructure, and daily life. This article explores the key trends surrounding the rainfall 2024, focusing on Africa, the United States, and global patterns.
The La Niña Effect: A Prominent Weather Driver
One of the major influencers of the 2024 rainy season is the transition from El Niño to La Niña, a climate phenomenon that greatly affects weather conditions worldwide. Historically, El Niño, characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, is often followed by La Niña, which brings cooler-than-normal temperatures and an increased likelihood of heavy rainfall in certain regions.
La Niña in Southern Africa
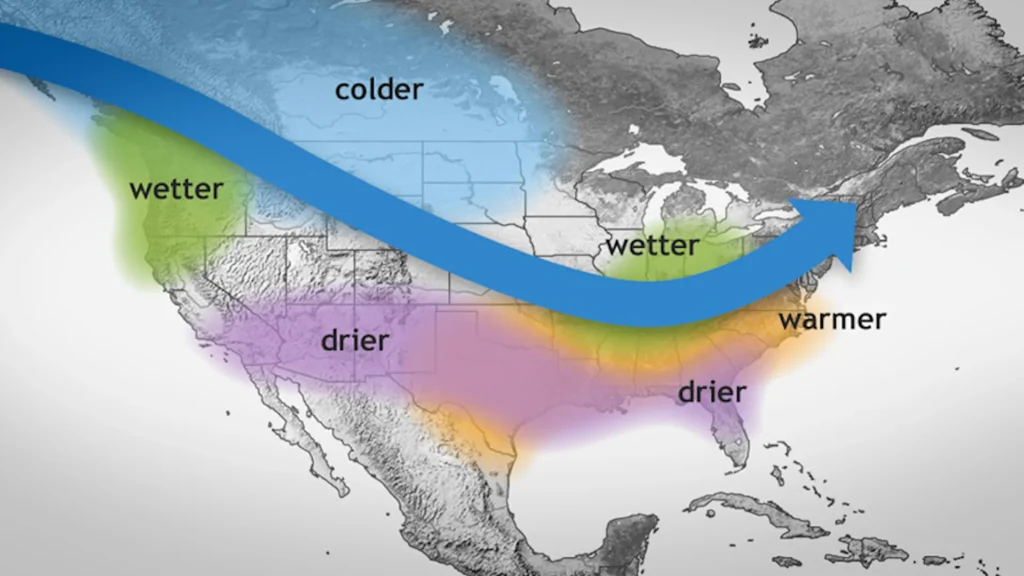
In Southern Africa, La Niña’s arrival is expected to bring normal to above-normal rainfall, reversing the devastating impacts of the El Niño-induced drought of the past year. Meteorological agencies, including those in Zimbabwe and Zambia, have forecasted a wetter rainy season from late 2024 through early 2025. This transition will provide a much-needed boost for agriculture, as farmers in countries like Zimbabwe and Zambia can expect better conditions for crop cultivation and pasture growth.
For Zimbabwe, in particular, the rains expected under La Niña’s influence are seen as a welcome relief, especially after years of drought that crippled crop yields and livestock health. La Niña is forecast to bring vigorous growth of pastures, benefiting livestock farmers. However, this shift also requires preparation, as the increased rainfall could lead to the proliferation of pests, such as ticks, and demand proper handling of water management and farming infrastructure
Impact on Agriculture

The forecasted rains hold substantial benefits for agricultural sectors across these regions. Crop production, especially maize, wheat, and rice, is expected to see improved yields, contributing to food security in areas that rely heavily on rain-fed agriculture. Farmers are being urged to prepare for the possibility of early planting to capitalize on the wet season’s full potential.
However, with the positives come challenges. Heavy rainfall can also increase the risks of flooding, which might damage crops and hinder transportation. Governments have warned of potential disruptions to the grain harvest in areas vulnerable to extreme rainfall events, emphasizing the need for disaster preparedness
The United States: Seasonal Rainfall and Travel Disruptions
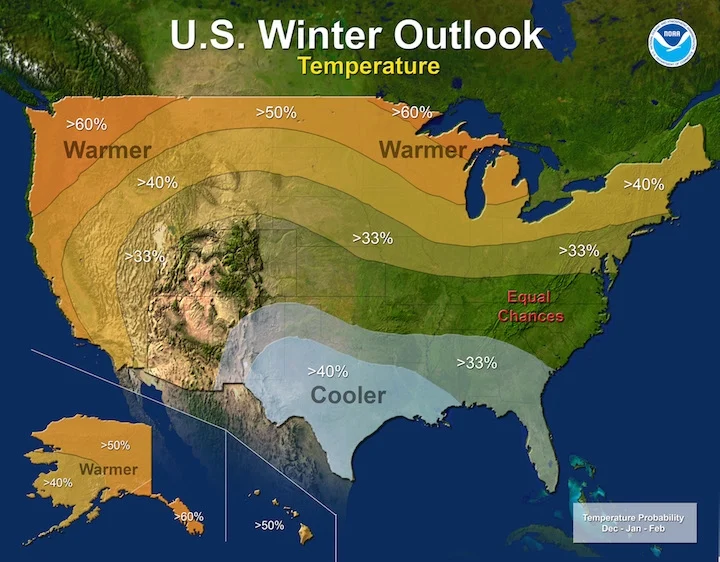
In the United States, rainy season forecasts also suggest significant impacts. In regions like the Tennessee Valley, Texas-Oklahoma, and the Pacific Northwest, December 2024 is expected to bring steady rain and snow, especially as we approach the winter solstice. This rainfall could lead to travel disruptions as holiday travelers may face wet roads and delayed flights due to storms.
In areas already experiencing a wet year, such as California, this wet season could add to the snowpack in the Sierra Nevada, helping with water reservoirs but potentially increasing the flood risks in areas already saturated from previous rains. Additionally, the Pacific Northwest is expected to see heavy precipitation during the holiday months, with Seattle and Portland bracing for continuous wet weather
Flood Risks and Infrastructure Challenges
While the rains are beneficial for water storage and agricultural needs, they also pose challenges. Urban areas, especially those with poor drainage systems, could face flooding and infrastructure strain. Floodwaters often overwhelm roads and disrupt local economies, particularly in already vulnerable regions. In addition, localized storms and severe flooding can pose risks to life and property.
Global Rainfall Trends: A Mixed Bag of Impacts
Globally, 2024’s rainy season is expected to bring a mixed bag of weather events, influenced by the ongoing climate crisis and shifting weather patterns. Some regions will experience excessive rainfall, while others may face drought-like conditions. This disparity makes it difficult for policymakers to predict the full scope of the wet season’s effects. However, scientists have noticed increasing variability in rainfall patterns, with some areas experiencing record rainfalls while others are left with drier-than-usual conditions.
In Southeast Asia, countries like Indonesia and the Philippines have already been dealing with intense rainfall during the monsoon season, which has led to flooding and landslides. In contrast, parts of Australia and Southern Europe are witnessing drier-than-average conditions, exacerbating concerns about droughts and water shortages.
Agriculture and Preparedness
Across the globe, agricultural stakeholders are increasingly aware of the risks tied to rain variability. Crops that depend on consistent rainfall, such as rice, corn, and coffee, are particularly vulnerable. Farmers are adjusting by diversifying their crops, investing in irrigation systems, and adopting water-efficient technologies to manage fluctuating rainfall patterns. Governments are also advising on the use of climate-resilient crops and early warning systems to help mitigate potential crop losses and ensure food security
Conclusion: Preparing for a Wet 2024
As we move forward into the wet season of 2024, regions around the world must prepare for both the benefits and risks of changing weather patterns. For areas expecting normal to above-normal rainfall, the focus should be on agricultural preparation, flood management, and infrastructure resilience. In countries like Zimbabwe, Zambia, and parts of the U.S., heavy rains could lead to enhanced crop production but also necessitate vigilance against flooding and pest outbreaks.
At a global level, climate change continues to influence rainfall variability, making it more critical than ever for countries to implement adaptive measures to handle the unexpected. As weather patterns continue to evolve, understanding these trends and preparing accordingly will help mitigate negative outcomes and capitalize on the opportunities provided by the wet season.
FAQs:
- What is La Niña and how does it affect rainfall patterns? La Niña is a climate phenomenon characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean. It often leads to increased rainfall in some areas, such as Southern Africa, and drier conditions in others.
- How does La Niña affect agriculture? La Niña generally brings good conditions for crop growth, especially in regions like Southern Africa. However, it can also increase the risk of flooding and pest infestations, which require careful preparation.
- Why is the wet season in 2024 so significant? This wet season of 2024 is significant due to the transition from El Niño to La Niña, which is expected to bring favorable conditions for agriculture in many parts of the world, particularly Africa.
- How will rainfall affect travel in the U.S. during the winter months? Heavy rainfall and snow are expected in parts of the U.S., including the Tennessee Valley and Pacific Northwest, potentially disrupting travel and holiday plans due to wet and hazardous conditions.
- What are the global implications of rainfall patterns in 2024? Global rainfall patterns in 2024 are expected to vary significantly, with some regions facing excessive rainfall and others dealing with droughts. This will have diverse effects on agriculture, infrastructure, and daily life.
- How can farmers prepare for the 2024 wet season? Farmers can prepare by early planting, investing in drainage systems, and using water-efficient technologies to manage changing rainfall patterns and reduce the risks of crop loss.
Do follow for more news: DailyForesight